mapmuts_parsecounts.py¶
Parses counts from alignments in the *_alignments.txt.gz file built by mapmuts_makealignments.py into
two text output files giving the counts of different nucleotide and codon identities.
To run this script from the prompt, first create a text infile of the
format described below. Then simply type mapmuts_parsecounts.py
followed by the infile name. For example, if the name is infile.txt,
type:
mapmuts_parsecounts.py infile.txt
The overlapping paired-end read alignments are used to call nucleotide identities. Nucleotides are called as follows:
- If both reads agree on the identity and neither relevant read position is in the exclusion lists specified in the input file (r1exclude or r2exclude), then the nucleotide is called at that identity using upper-case nucleotides, for example ‘A’ or ‘T’.
- If one read specifies an identity and the other read gives an ‘N’ or is at an excluded position, the identity is called to the lower-case value of the read the specifies an identity. For example, a position might be called to ‘a’ or ‘t’.
- If the two reads specify different identities, or if both specify an N or have the position excluded, a position is called to ‘N’
Codons are called to the constituent nucleotides using the aforementioned scheme. Codons for which only partial nucleotide coverage is achieved are not called.
If pylab / matplotlib are available, summary plots are also generated. If pdflatex is available, these plots are merged into a summary PDF document as well.
Input file format¶
The input file specifies key / value pairs on individual lines in the format:
key1 value1
key2 value2
Blank lines or lines that begin with # are ignored (i.e. as comment lines). The input file should contain the following keys:
- alignmentfile specifies the name of a
*_alignments.txt.gzfile built by running mapmuts_makealignments.py. - fullgenefile specifies the name of the file containing the full target amplicon to which the reads were aligned. This should be a FASTA file containing a single sequence. This should be the same sequence used when running mapmuts_makealignments.py to make alignmentfile.
- generange specifies region of the amplicon that contains the the coding sequence. This should be two number specifying the first and last nucleotide of the sequence in fullgenefile that are part of the coding sequence in 1, 2, ... numbering. This should be the same value of generange used when running mapmuts_makealignments.py. to make alignmentfile. The gene must be a valid coding sequence that can be translated; the terminal stop codon should not be included.
- upcase specifies how we handle possible upper / lower case differences in nucleotide codes. This is crucial because of the case-dependent coding of nucleotide identities (with upper-case indicating definitively called by both reads, and lower case indicating called by just one read). If upcase is True, then all sequences are converted to upper case before alignment. This is the safest option, but is also the slowest since it requires so many case conversions. If upcase is test, then the gene sequence is converted to upper case, and the alignment file is tested to make sure the first entry is upper case. If the first entry is upper case, no case conversion is done on the alignments, which will be faster. If the first entry is not upper case, then an exception is raised, and you wil probably have to switch this option to True.
- r1exclude specifies read position in the R1 read that are excluded from the analysis. You might want to exclude a position of the results of mapmuts_makealignments.py make clear that certain read positions have very high error rates (numbers of mismatches) relative to other positions. If no positions are being excluded, enter None. If positions are being excluded, list the numbers separated by spaces of the positions to exclude in 1, 2, ... numbering.
- r2exclude is like r1exclude, but for the R2 read.
- outfileprefix specifies the prefix appended to all file names created by this method. The specific files and their suffixes are described in the section on the output files below. Any existing output files are overwritten.
- samplename specifies the name of the sample for this run of the script. Name are allowed to contain spaces.
Here is an example input file:
# Example input file to mapmuts_parsecounts.py
alignmentfile sample_1_alignments.txt.gz
fullgenefile Aichi68-NP_amplicon.fasta
generange 62 1555
upcase test
r1exclude None
r2exclude 2 3 48 49
outfileprefix example_run
samplename example run
Output files¶
Running this script produces a series of output files. The names of these files consist of the prefix specified by outfileprefix in the input file, then the indicated suffix. Any existing files are overwritten. The output files:
outfileprefix_parsecounts_log.txt : a text file that tracks the output of this script.
outfileprefix_ntcounts.txt : A file listing the number of occurrences of each nucleotide at each position. Has the following columns:
- POSITION : the nucleotide position in 1, 2, ... numbering.
- WT : wildtype nucleotide identity, upper case
- COUNTS : total number of times this position is covered by an an aligned read pair in alignmentfile.
- all nucleotide codes (A, T, C, G, a, t, c, g, N) : number of times the reads call the nucleotide to each of these identities. A, T, C, and G represent nucleotides called to the same identity by both reads. a, t, c, and g represent nucleotides called by one read, with the other ambiguous or in the r1exclude or r2exclude list for that read position. N represents nucleotides called to conflicting values by both reads, or ambiguous or excluded in both reads.
outfileprefix_codoncounts.txt : A file like outfileprefix_ntcounts.txt but for codon positions. Codons are called to identities of their substituent nucleotides. If some of the nucleotides in a codon are not called, no identity is called for the codon.
outfileprefix_aacounts.txt : A file giving the number of occurrences of each amino acid among the definitively called codon (both reads agree, indicated by upper case codon in outfileprefix_codoncounts.txt) for each position.
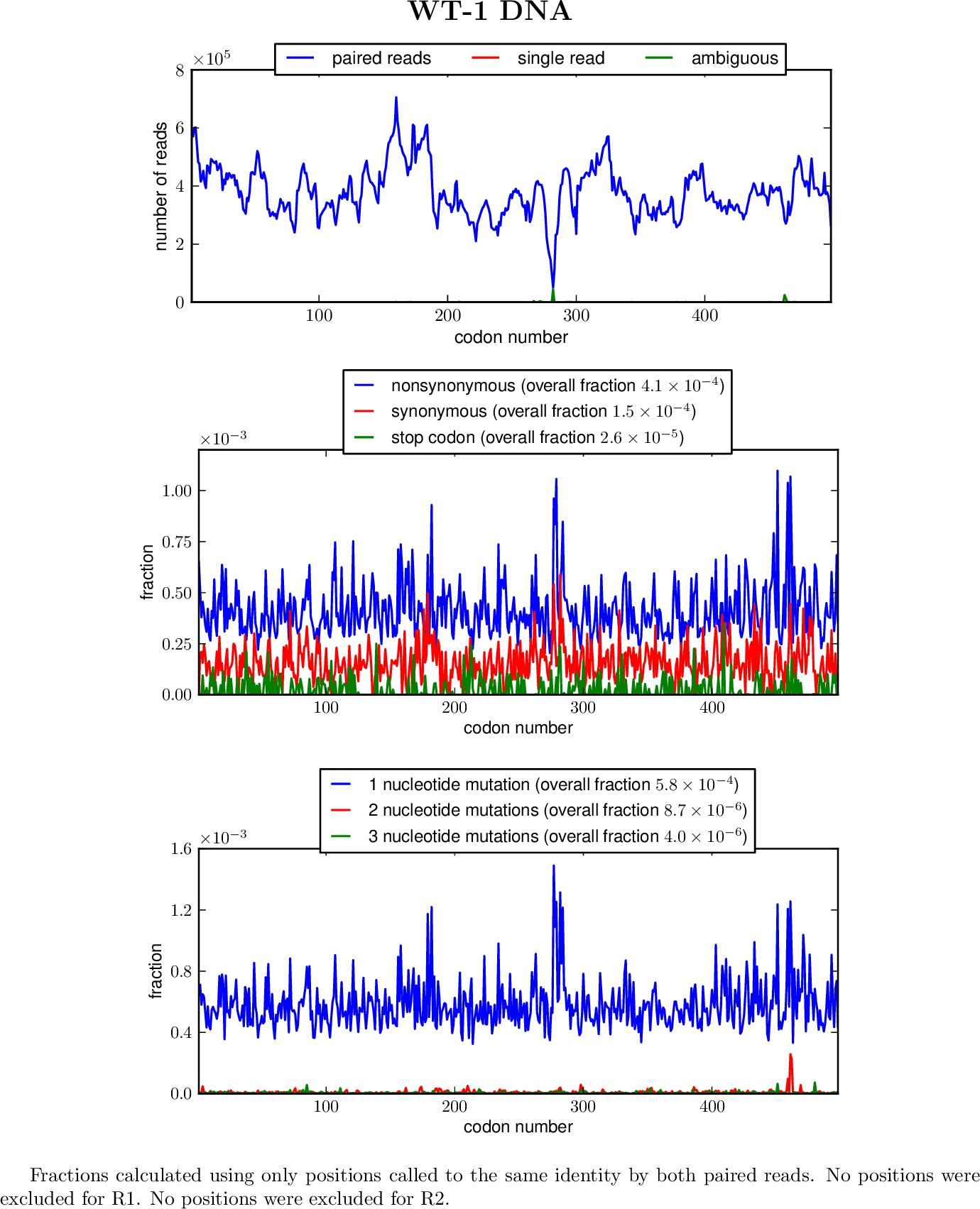
outfileprefix_codondepth.pdf : Created if pylab / matplotlib is available, a graphical summary of read depth at each codon position.
outfileprefix_syn-ns-dist.pdf : Created if pylab / matplotlib is available, a graphical summary of distribution of synonymous and nonsynonymous mutations among all definitively called (by both reads) mutations.
outfileprefix_nmutspercodon-dist.pdf : Created if pylab / matplotlib is available, a graphical summary of the distribution of number of nucleotide mutations per codon mutations among all definitively called (by both reads) codons.
outfileprefix_parsesummary.pdf : Created if pylab / matplotlib and pdflatex are available, an overall graphical summary of the results of the alignment parsing.